Welcome back to a new case study. This case study shows the work out laboratory does for a patients with lymphoma.
So sit back and grab a cuppa!!
A patient sample was run on our Navios Flow Cytometer.


Results were obtained where the patient showed to have a CD19 (B cells) count result of <1 cell/µL. The reference range for CD19 is: 100 – 500 cells/µL. A result of <1 shows low or absent B cells. Given information mentioned that the patient is also on Rituximab. Rituximab is one of a number of man-made antibodies that can be used to treat disorders of the immune system (biologic therapy).
The patient is showing low B cell count due to Rituximab, which is used in the treatment of lymphoma. This is because Rituximab targets a surface protein that is found specifically on B cells (CD20). The drug causes signalling of apoptosis, complement activation and cell mediated cytoxicity. This is the cause of the reduction in B cells within this patient and reduces the leukaemic B cells and the progression of the disease.
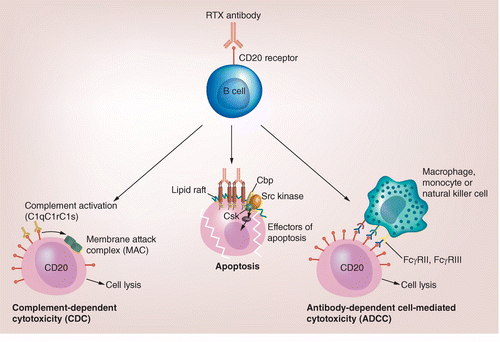
Our role in monitoring the patient
In the immunology laboratory we play a role in measuring the patient B cells In the immunology laboratory we play a role in measuring the patient B cells by flow cytometry. We also use flow cytometry to detect the markers that are more generally used to decide whether a patient has lymphoma or not. We test a number of markers together (known as a panel) so that we can determine what is known as the ‘immunophenotype’. From this, the clinician can decide whether a patient has an acute or chronic lymphoma (or leukaemia) and what type of cell it has been formed from.
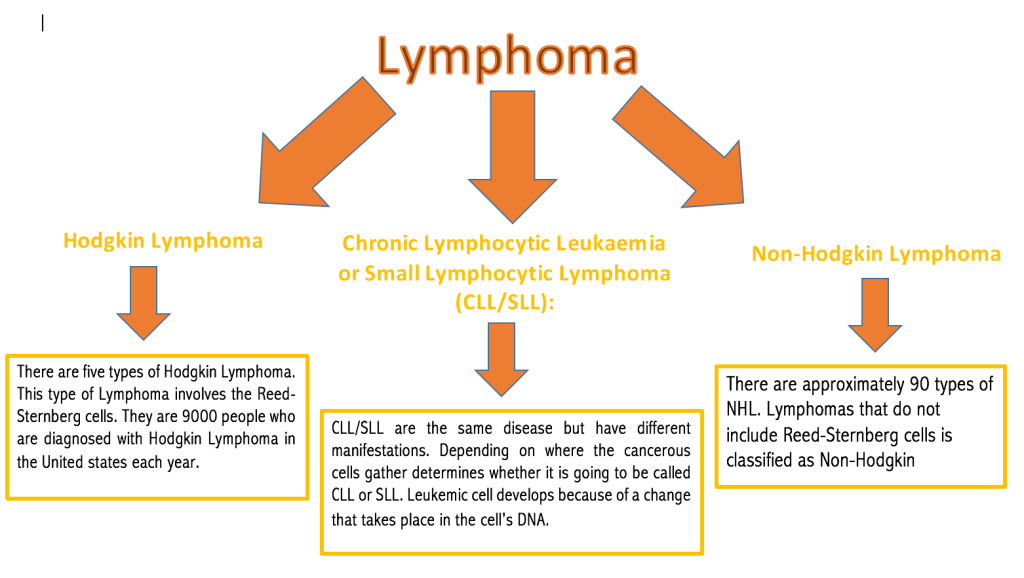
Types of Lymphoproliferative disorder
If left untreated patients suffering from Lymphoma will die due to organ failure and infections that their immune system cannot fight.
Treatment
There is a variety of treatment options available for lymphoma patients and each individual patient is treated according to their conditions.
Those with Hodgkin lymphoma are treated with chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy or a combination of these. Patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma will receive a form of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, biologic therapy, immunotherapy or a combination of these. On some occasions bone marrow, stem cell transplantation or CAR T-Cell therapy can be used.
Other therapies that have been developed for the treatment of lymphoproliferative disorders include:

Thank you in taking your time in reading. I hope the information was beneficial for all of you and an insight in the work we do. Please leave a comment, subscribe and share.
Leave a comment